Experimental and Computational Assessment of Adsorbates in Ultraclean 2D MoS2(1–x)Se2x Nanosheets Treated by Ethanol for Enhanced Photodetector Applications

Dipak Maity, Ravi K. Biroju, Viliam Vretenár, Mihir Ranjan, Sahoo, L’ubomír Vančo, Matej Mičušík, Tharangattu N. Narayanan, Kalpataru Pradhan
In: ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2025, 8, 47, 22573–22585
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.5c03601
Abstract
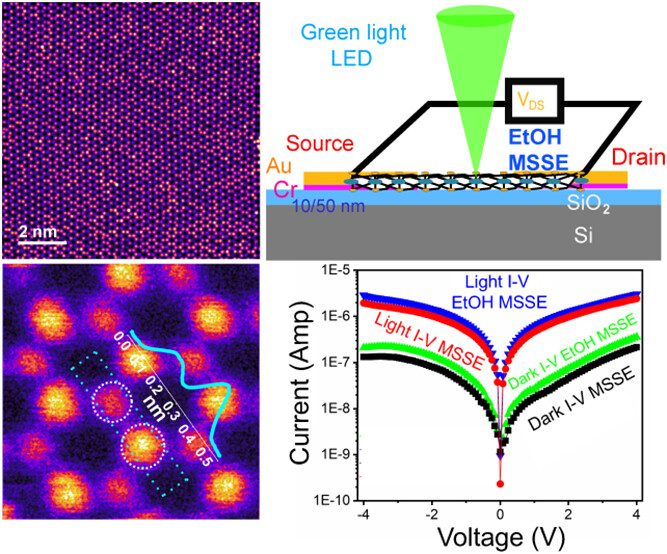
Two-dimensional semiconductor-transition-metal dichalcogenide (2D-STMD) based semiconductors have emerged as promising materials for future spintronic and optoelectronic applications, including photodetectors and transistors. Transferring high-quality chemical vapor deposition (CVD)-grown monolayer 2D-STMDs and their alloys to the target substrate is very challenging for fabricating efficient devices. Unfortunately, current post-transfer methods struggle to completely remove unwanted contamination residues during wet-transfer processes, which adversely affects material quality and intrinsic properties. In this work, the effect of ethanol cleaning on the qualitative and quantitative assessment of molecular adsorbates is demonstrated, based on atomic-resolution high-angle annular dark field scanning transmission electron microscopy (HAADF-STEM) image analysis supported by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Auger electron spectroscopy (AES), and density functional theory (DFT) calculations, which showcases ultraclean material structures. We estimate the unidentified molecular adsorbates in the proximity of molybdenum (Mo) and chalcogen (S, Se) atomic sites, which are tentatively assigned as ‘C2H5OH (EtOH)’, ‘H2O’, and ‘O2’ related adsorbates. The attribution is based on HAADF-STEM Gaussian line shape fitting of atomic intensity columns and corresponding computed adsorption energy values after ethanol treatment of the MoS2(1–x)Se2x (MSSE) alloy. In line with experimental observations of persistent OH-containing residues on the surface, DFT simulations show that EtOH has better adsorption on both pristine and sulfur-vacancy MSSE monolayers than H2O and O2. Photodetector device measurements revealed a remarkable ∼90% enhancement in photocurrent values for ultraclean samples, significantly boosting the material’s photoresponsivity. DFT calculations on the adsorption energy and density of electronic states were also conducted to validate our experimental findings.